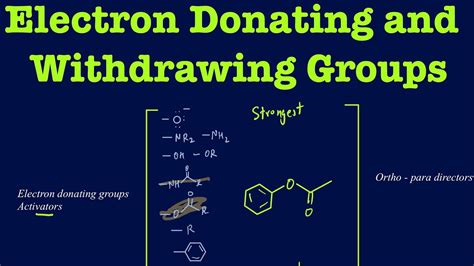
electron donating and withdrawing groups list|6.4.2: All other things being equal, electron withdrawing groups : Tagatay Activating groups increase the rate. Deactivating groups decrease the rate. EDG = electron donating group. EDG can be recognised by lone pairs on the atom adjacent to the π system, eg: -OCH 3. except - R, -Ar or -vinyl (hyperconjugation, π electrons) . See PinoyKangkarot's porn videos and official profile, only on Pornhub. Check out the best videos, photos, gifs and playlists from amateur model PinoyKangkarot. Browse through the content she uploaded herself on her verified profile. Pornhub's amateur model community is here to please your kinkiest fantasies.
PH0 · Inductive Effects of Alkyl Groups
PH1 · Electrophilic aromatic directing groups
PH2 · Electron
PH3 · Effects of Electron
PH4 · Ch12 : Substituent Effects
PH5 · Activating and Deactivating Groups In Electrophilic Aromatic
PH6 · 6.4.2: All other things being equal, electron withdrawing groups
PH7 · 18.6: Substituent Effects on the EAS Reaction
PH8 · 14: Substituent Effects
Belfast is situated on the north-east coast of the island of Ireland. As the capital of Northern Ireland, the city is part of the United Kingdom, and separate from the Republic of Ireland – a .
electron donating and withdrawing groups list*******Activating groups increase the rate. Deactivating groups decrease the rate. EDG = electron donating group. EDG can be recognised by lone pairs on the atom adjacent to the π system, eg: -OCH 3. except - R, -Ar or -vinyl (hyperconjugation, π electrons) .Substituent Effects(contd.) . There are two main electronic effects that substituents . Pi ( π) Donors and Acceptors (often just called “Resonance”) Oxygen And Nitrogens Containing Lone Pairs Are Highly Activating When Bonded Directly To The .Although the full electronic structure of an arene can only be computed using quantum mechanics, the directing effects of different substituents can often be guessed through analysis of resonance diagrams. Specifically, any formal negative or positive charges in minor resonance contributors (ones in accord with the natural polarization but not necessarily o.
6.4.2: All other things being equal, electron withdrawing groups For electron withdrawing groups, all of the sigma complexes are destabilized. The meta-position is the least destabilized and produces the largest percentage of the reaction products. Acetophenone will be used .
The conjugate bases of many Brønsted superacids have electron-withdrawing substituents that make them such poor Lewis bases that they are useful as .Examples of good electron donating groups are groups with lone pairs to donate, such as: The oxygen anion, -O-Alcohol groups, -OH Amine groups, -NH 2 or -NR 2; .
Properties of Arenes. Inductive Effects of Alkyl Groups. Expand/collapse global location. Inductive Effects of Alkyl Groups. Page ID. A substituent on a benzene ring can effect the placement of additional .
Substituent groups can be electron withdrawing or electron donating. Electron Withdrawing Groups. Because F pulls electrons toward itself, and positively polarizes . The effect of electron-donating (E.D.) groups on porphyrins and allyliporphyrins was further investigated. Contrary to the initial assumption that the E.D. .
To clarify what is meant by electron-donating and electron-withdrawing substituents: Any substituent whose first atom (the one that's attached to the benzene .electron donating and withdrawing groups list To clarify what is meant by electron-donating and electron-withdrawing substituents: Any substituent whose first atom (the one that's attached to the benzene . In general, Diels-Alder reactions proceed fastest with electron-withdrawing groups on the dienophile (diene lover). Ethylene reacts slowly while propenal, ethyl propenoate, and other molecules shown below are highly reactive in a Diels-Alder reaction.. In much the same manner as electron-withdrawing substituents on a benzene ring, .
electron donating and withdrawing groups list 6.4.2: All other things being equal, electron withdrawing groups The important electron withdrawing groups should be remembered for NEET examination point of view are halogens (F, Cl), nitriles CN, carbonyls RCOR’ and nitro groups NO 2. The electron donating groups are alkyl groups, alcohol groups and amino groups. EWGs (electron withdrawing groups) are highly affine to electrons. The main point to remember here is that electron-donating groups direct substitution to the ortho and para positions, while pi electron-withdrawing groups direct substitution to the meta position. To clarify what is meant by electron-donating and electron-withdrawing substituents: Any substituent whose first atom (the one that's .Nov 28, 2009. #2. Electron donating groups generally have a lone pair on the atom directly bonded to the aromatic ring. Examples include: OH, NR2, OR, NHCOR (amides), OCOR (esters), and alkyl groups. Electron withdrawing groups make it more difficult to introduce new groups onto the ring. Examples include: COR, NO2, CN, CONH2, and NH3.
The reactivity of aromatic pi bonds in S E Ar reactions is very sensitive to the presence of electron-donating groups (EDG) and electron-withdrawing groups (EWG) on the aromatic ring. This is due to the carbocation nature of the intermediate, which is stabilized by electron-donating groups and destabilized by electron-withdrawing groups .Here are some general pointers for recognising the substituent effects: The H atom is the standard and is regarded as having no effect. Activating groups increase the rate. Deactivating groups decrease the rate. EDG = electron donating group. EDG can be recognised by lone pairs on the atom adjacent to the π system, eg: -OCH 3. In the previous episode we discussed what happens when we use electrophilic aromatic substitution to add a group to a benzene ring, but what happens when you.Electron with-drawing groups can decrease the electron density at the nucleus, deshielding the nucleus and result in a larger chemical shift. . The effects are cumulative so the presence of more electron withdrawing groups will produce a greater deshielding and therefore a larger chemical shift, i.e. Compound: CH 4: CH 3 Cl: CH 2 Cl 2: CHCl 3 .
Substituents (14.1B) Here are some specific examples of substituents and reactions or properties they affect: Cl-CH2-CO2H is a stronger acid than H-CH2-CO2H. The substituent is Cl and the property is the acidity of the CO2H group (Figure 14.01). Figure 14.01. Methoxybenzene is nitrated more rapidly than benzene. Here, Y is an electron-donating group or + I group because it donates electrons to Carbon. This effect is also known as a positive inductive effect (+ I effect) or electron-donating inductive effect. . Illustration 2: Demonstrates that electron-withdrawing groups (EWG) increase acidity, while electron-donating groups (EDG) .

Correct answer: −NMe3. Explanation: The above reaction would more readily proceed if the electrophilicity of the carbonyl carbon were enhanced. This may be achieved through electron withdrawal via the R group. The ether (-OMe), the methyl (-Me), and the hydroxyl (-OH), would all produce a electron-donating effect, and are thus incorrect answers.
CHEM 202. EDG v. EWG. • To know the strength of the withdrawing or donating group look to see if the electrons are being “shared”. o Example: An ester vs. a ketone. While they are both withdrawing groups, a ketone is a stronger withdrawing group than an ester. A ketone can only pull electrons from the ring, where the carbonyl of the ester .
An electron-withdrawing group ( EWG) is a group or atom that has the ability to draw electron density toward itself and away from other adjacent atoms. [1] This electron density transfer is often achieved by resonance or inductive effects. Electron-withdrawing groups have significant impacts on fundamental chemical processes such as acid-base .Substituent groups can be electron withdrawing or electron donating. Electron Withdrawing Groups. Because F pulls electrons toward itself, and positively polarizes the C to which it is bonded, it is called an inductive electron withdrawing group (EWG). The other halogen atoms, as well as the NO2 group (Table 14.02), are also inductive EWGs . In many cases, this conjugate base was an anion – a center of excess electron density. Anything that can draw some of this electron density away– in other words, any electron withdrawing group – will stabilize the anion. Conversely, a carbocation is stabilized by an electron donating group, and destabilized by an .Inductive effect. In chemistry, the inductive effect in a molecule is a local change in the electron density due to electron-withdrawing or electron-donating groups elsewhere in the molecule, resulting in a permanent dipole in a bond. [1] It is present in a σ (sigma) bond, unlike the electromeric effect which is present in a π (pi) bond . Determining the aromaticity of various fluorinated benzenes is challenging as easily obtained experimental aromaticity [Δδ(Houter – Hinner)] necessitates the chemical shifts of inner and outer protons. This issue was addressed in porphyrinoids by replacing the electron-withdrawing (E.W.) groups at the meso-positions of porphyrins and . https://joechem.io/videos/23 for video on jOeCHEM and attached worksheet + solution (below video on jOeCHEM aka the link). Worksheet: http://worksheets.joec.
aws s3 ls s3://MyBucket To list object from a folder you need to execute command as - aws s3 ls s3://MyBucket/MyFolder/ This above command lists object that reside inside folder named MyFolder. To get an objects list from such a logical hierarchy from Amazon S3, you need specify the full key name for the object in the GET operation.
electron donating and withdrawing groups list|6.4.2: All other things being equal, electron withdrawing groups